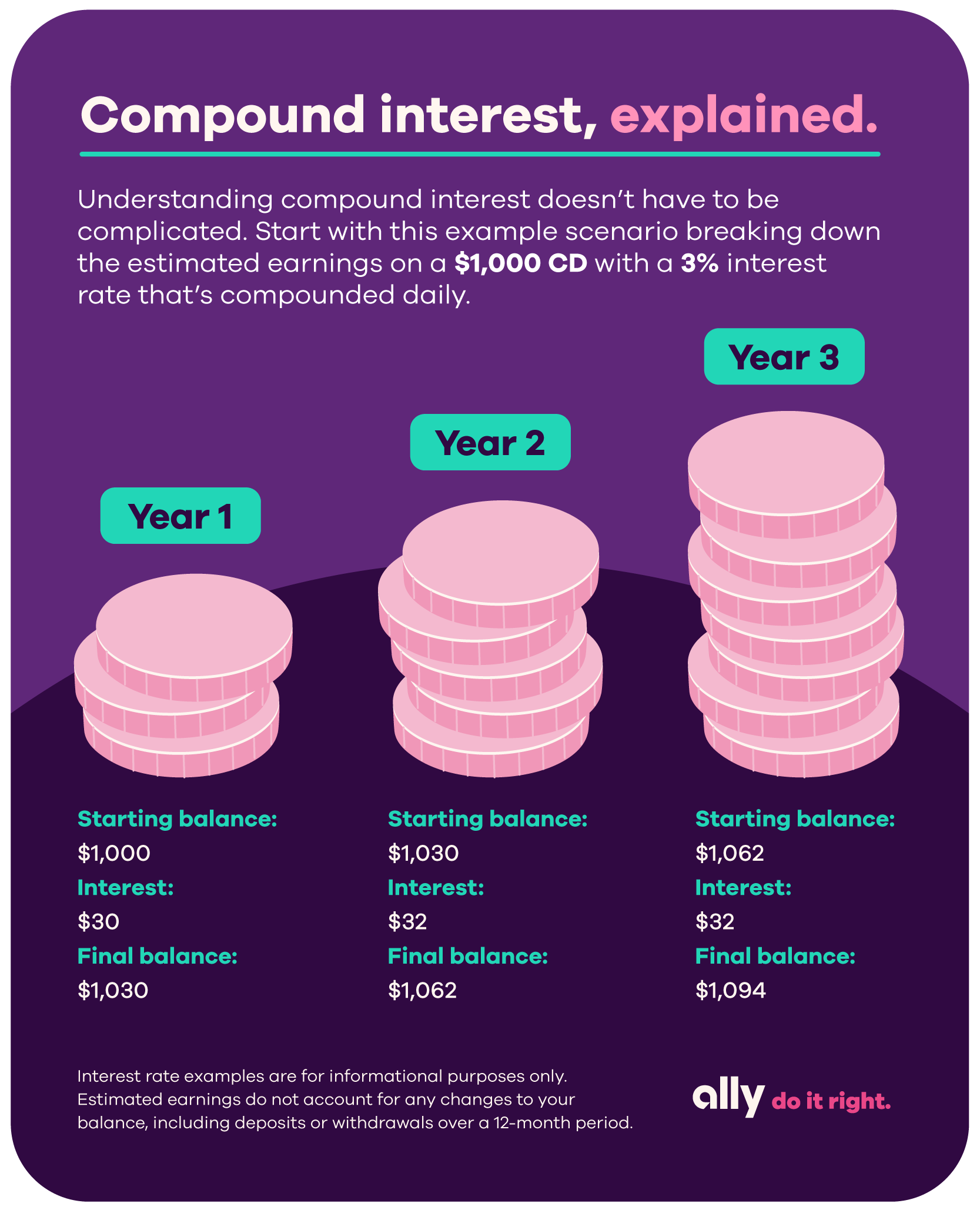
Imagine your money growing day and night, whether you’re sleeping or out enjoying life, and growing exponentially! That’s the power of compound interest. Known as interest on interest, compound interest is a financial concept that can transform your savings or investments into significant wealth. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, anyone can leverage compound interest by investing smartly. Saving for retirement, a home, or managing a loan? Understanding the compound interest definition is key to financial success.
In this guide, we’ll explore what Compound interest is, the compound interest formula, and why it’s called the “eighth wonder of the world.” We’ll share compound interest examples with solutions, compare compound interest vs simple interest, and provide tips to maximize your earnings. Plus, we’ll answer common questions and recommend a free compound interest calculator to plan your financial future. Let’s dive in!
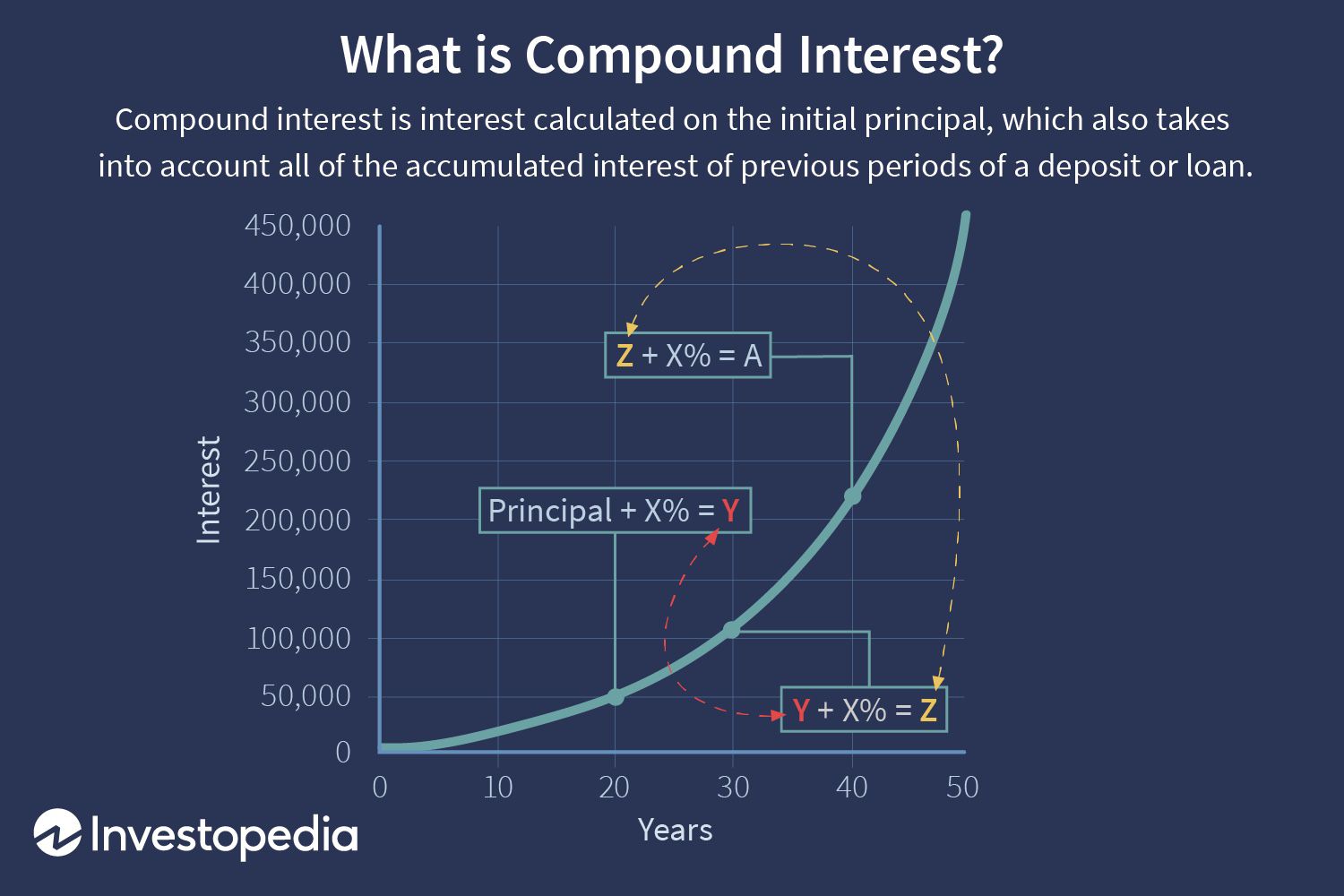
Definition :
Compound interest is the interest earned on your initial investment (principal) and the interest that accumulates over time. Unlike simple interest, which is calculated only on the principal, compound interest accelerates your money’s growth because the interest you earn starts earning interest too. This Compound interest definition highlights its exponential growth potential.
Example: Invest $1,000 at a 5% annual compound interest rate, compounded yearly. In year one, you earn $50 interest. In year two, the calculation of compound interest is done on $1,050 (principal + $50), giving you $52.50. This snowball effect drives massive growth over time.
Albert Einstein reportedly said, “Those who understand compound interest earn it; those who don’t, pay it.” Whether saving, investing, or borrowing, compound interest quietly shapes your finances.
How Does the Compound Interest Formula Work?
The Compound interest formula calculates how your money grows by adding interest to the principal at regular intervals, like monthly or yearly, creating a larger base for future interest. The frequency of compounding—daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually—affects your compound interest gains. More frequent compounding means faster growth.
How It Works:
Principal: Your starting amount, like $1,000.
Interest Rate: The percentage applied, like 5%.
Compounding Frequency: How often interest is added (daily, monthly, yearly).
Time: The longer your money stays invested, the bigger the compound interest effect.
The compound interest formula is:
[A = P \left(1 + \frac{r}{n}\right)^{nt}]
Where:
A = Final amount (principal + compound interest)
P = Principal (initial investment)
r = Annual interest rate (decimal, e.g., 5% = 0.05)
n = Number of times compound interest is applied per year (1 for yearly, 12 for monthly, 365 for daily)
t = Time in years
Compound Interest Earned: A – P
This compound interest formula is the key to the calculation of compound interest. Let’s explore it with compound interest examples.
Compound Interest vs Simple Interest ?
To understand Compound interest vs simple interest, know that simple interest is calculated only on the initial principal, while compound interest includes interest on both the principal and accumulated interest, leading to exponential growth.
Comparison:
Simple Interest Formula: Interest = Principal × Rate × Time (I = P × r × t)
Compound Interest Formula: Interest is calculated on the principal plus accumulated interest.
Compound Interest Formula Example: Invest $1,000 at 5% for 3 years:
Simple Interest: I = 1000 × 0.05 × 3 = $150. Total = $1,150.
Compound Interest (Yearly): A = 1000 × (1 + 0.05/1)^(1×3) = $1,157.63.
The difference seems small at first, but over time, compound interest significantly outperforms simple interest, especially for long-term compound interest investments.
Why Compounding Frequency Matters for Compound Interest?
The frequency of Compound interest—how often interest is added—impacts your returns. Common frequencies include:
- Yearly: Once a year
- Quarterly: 4 times a year
- Monthly: 12 times a year
- Daily: 365 times a year (use a compound interest daily calculator for precision)
- Continuously: Infinite times (using A = P × e^(rt), where e ≈ 2.718)
- Compound Interest Example: $1,000 at 5% for 10 years:
- Yearly: A = 1000 × (1 + 0.05/1)^(1×10) = $1,628.89
- Monthly: A = 1000 × (1 + 0.05/12)^(12×10) = $1,647.01
- Daily: A = 1000 × (1 + 0.05/365)^(365×10) = $1,648.66
Frequent compound interest boosts returns, even with the same rate and time.
Compound Interest Examples with Solutions:
Here are practical compound interest examples to show how it works:
Example 1: Savings Account
You deposit $5,000 in a savings account with 4% annual compound interest, compounded monthly, for 5 years.
[A = 5000 \left(1 + \frac{0.04}{12}\right)^{12 \times 5} = $6,104.95]
Compound Interest earned: $6,104.95 – $5,000 = $1,104.95.
Example 2: Compound Interest Investments
You invest $10,000 in a mutual fund with 8% annual compound interest, compounded yearly, for 20 years.
[A = 10000 \left(1 + \frac{0.08}{1}\right)^{1 \times 20} = $46,609.60]
Compound Interest earned: $46,609.60 – $10,000 = $36,609.60.
Example 3: Loan
You borrow $20,000 at 6% annual compound interest, compounded monthly, for 3 years. Use a compound interest loan calculator for quick results.
[A = 20000 \left(1 + \frac{0.06}{12}\right)^{12 \times 3} = $23,933.60]
Compound Interest paid: $23,933.60 – $20,000 = $3,933.60.
These compound interest examples with solutions show how compound interest grows savings but increases loan costs.
Pros and Cons of Compound Interest
Pros
- Exponential Growth: Compound interest grows money faster than simple interest.
- Wealth Building: Ideal for long-term compound interest investments like retirement or mutual funds.
- Passive Income: Earn compound interest effortlessly through savings or bonds.
- Flexible Compounding: Choose frequencies to maximize compound interest returns.
Cons
- Costly for Loans: Compound interest on loans or credit cards can be expensive.
- Time-Dependent: Needs long periods for significant compound interest gains.
- Market Risks: Compound interest investments like stocks carry risks.
- Complex Calculations: Manual calculation of compound interest is tough without a compound interest calculator.
Tips to Maximize Compound Interest
- Start Early: Invest early to let compound interest work longer. Small amounts grow big over time.
- Choose Frequent Compounding: Pick accounts with monthly or daily compound interest for better returns.
- Reinvest Earnings: Don’t withdraw interest or dividends; reinvest to boost compound interest.
Use a Compound Interest Calculator: Try the MoneyCalculator Compound Interest Calculator to plan your compound interest earnings.
Pay Off High-Interest Debt: Clear loans or credit cards quickly to avoid costly compound interest.
Diversify Investments: Spread money across stocks, bonds, and savings to balance compound interest risks and rewards.
Is Compound Interest the Best Strategy?
Compound interest is a powerful tool, but not perfect for every situation. It excels in long-term, low-risk compound interest investments like savings accounts, bonds, or index funds. However, stocks or mutual funds with compound interest carry market risks. For short-term goals or high-risk investments, other strategies may work better. Evaluate your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon when using compound interest.
Join The Finance Newsletter :
- Want more ideas and step-by-step business ideas guidance ?
Join The Finance newsletter – Subscribe My Free newsletter to help you build your dream business in 2025.
Use My Free Compound Calculator Tools for Your Future Growth: Money Calculator
FAQs (Frequently Asked Question):
What is the difference between compound interest and simple interest?
Compound interest is calculated on the principal plus accumulated interest, while simple interest is only on the principal.
Is compound interest safe?
As a concept, compound interest is safe in low-risk options like savings accounts or government bonds. Stocks, however, involve risks.
How do I calculate compound interest?
Use the compound interest formula A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt) or a compound interest online calculator like MoneyCalculator.
Is compound interest better for long-term or short-term investments?
Compound interest is best for long-term investments due to its exponential growth over time.
Can compound interest make me rich?
With consistent investments, high rates, and long durations, compound interest can significantly grow wealth, but it depends on smart choices and isn’t a quick-rich scheme.
Conclusion :
Compound interest is a financial superpower that can turn small savings into massive wealth. By earning compound interest on your principal and its interest, it creates a snowball effect perfect for long-term goals like vacations, homes, or retirement. Mastering the compound interest definition and compound interest formula sets you up for financial success.
Start early, choose frequent compound interest options, and use a compound interest calculator like Money Calculator to plan—it’s free and easy! With the right strategy, compound interest can be your financial best friend, but a wrong move can make it costly. Ready to unlock the power of compound interest? Start today and let your money work for you for life!